![]() The primitive
intestine starts to grow at the 3rd week of embryonic development.
The primitive
intestine starts to grow at the 3rd week of embryonic development.
At this time, the extra embryonic coelom invaginates into the embryo under the influence of tranversal and longitudinal plicatures to bound from inside to outside respectively : the primitive bowel, the vitellin canal and the yolk sac (figure 1b).
From top to bottom, the primitive intestine is made up of three parts:
Anterior intestine that will give the pharyngeal gut, the broncho-pulmonary tract, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, liver, biliary tract, and pancreas. This part of intestine is vascularized by the celiac trunk and supported by the mesoduodenum.
Medium intestine, represented by the primitive intestinal loop which communicates with the vitellin canal. This segment will constitute the distal part of the duodenum, the small intestine, the cecum, the appendix and the proximal two-thirds of the transverse colon. Is is supported by the "common mesentery".
Posterior intestine, that constitutes the distal third of the transverse colon, the left colon, the sigmoïd colon, rectum and superior two-thirds of the anal canal. The distal part opens into the cloaca common with the urogenital sinus. This cloaca will divide later in two parts. This segment is supported by the primitive mesocolon.
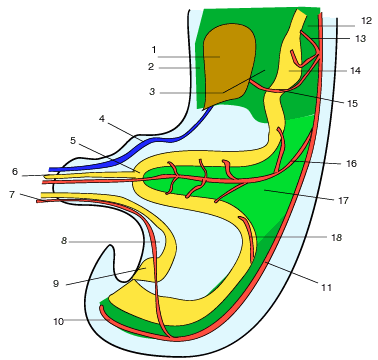
Fig 2
Figure 2 : Schematic sagittal view of an embryo's abdomen at the 6th week of intra uterine development (from Kamina and DiMarino):
1 Liver (hepar)
2 Ventral mesogastrium (falciform ligament)
3 Ventral mesogastrium (small omentum)
4 V. umbilicalis
5 Umbilical loop (ansa intestinalis primitiva)
6 Vitelline duct (canalis vitellinus or omphalo-mesenteric duct)
7 A.umbilicale
8 Mésocyst
9 Urogenital sinus
10 a. sacrales media)
11 Aorta
12 Dorsal mesogastrium
13 a. gastrica
14 Stomach (ventriculis)
15 a. gastrica dextra
16 a.mesenterica sup.
17 Common Mesentery
18 A. mesenterica inf.